-40%
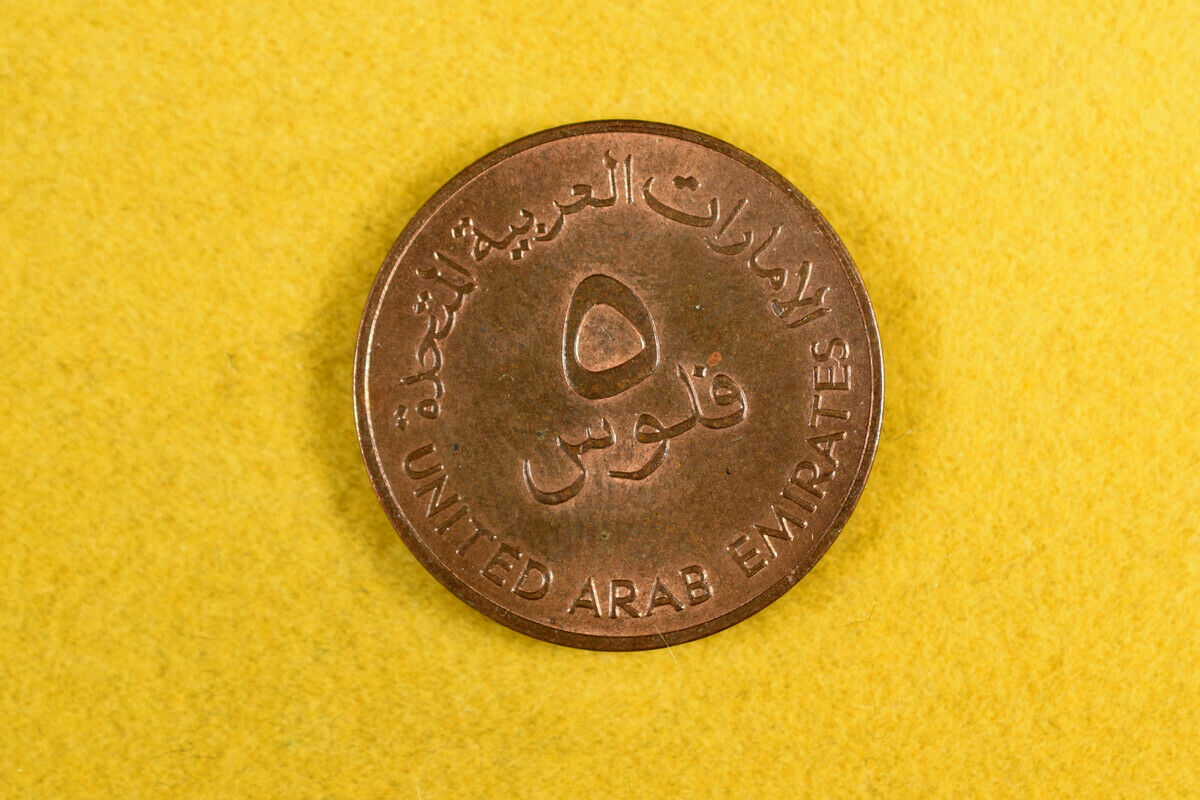
United Arab Emirates 25 Fils - Khalifa magnetic sand gazelle UAE Cool Islam coin
$ 1.47
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
coin seen is an example dates will varyCountry United Arab Emirates
Type Standard circulation coin
Years 1435-1440 (2014-2018)
Calendar Islamic (Hijri)
Value 25 Fils
0.25 AED = 0.07 USD
Currency Dirham (1973-date)
Composition Nickel plated steel
Weight 3.48 g
Diameter 20 mm
Thickness 1.5 mm
Shape Round
Orientation Medal alignment ↑↑
References KM# 4a
Obverse
Denomination in Arabic characters surrounded by name of the country
Lettering:
الامارات العربية المتحدة
٢٥
فلساً
UNITED ARAB EMIRATES
Translation:
United Arab Emirates
25
Fils
United Arab Emirates
Reverse
Gazelle facing left, date below. Probably the sand gazelle or goitered gazelle (Gazella subgutturosa marica), one of the 2 species found in the UAE
Lettering: ١٤٣٥-٢٠١٤
Translation: 2014-1435
Engraver: Geoffrey Colley
Edge
Reeded
The United Arab Emirates (UAE; Arabic: الإمارات العربية المتحدة al-ʾImārāt al-ʿArabīyyah al-Muttaḥidah), sometimes simply called the Emirates (Arabic: الإمارات al-ʾImārāt), is a country in Western Asia at the northeast end of the Arabian Peninsula on the Persian Gulf, bordering Oman to the east and Saudi Arabia to the south and west, as well as sharing maritime borders with Qatar to the west and Iran to the north. The sovereign constitutional monarchy is a federation of seven emirates consisting of Abu Dhabi (which serves as the capital), Ajman, Dubai, Fujairah, Ras Al Khaimah, Sharjah and Umm Al Quwain. Their boundaries are complex, with numerous enclaves within the various emirates.[8] Each emirate is governed by a ruler; together, they jointly form the Federal Supreme Council. One of the rulers serves as the President of the United Arab Emirates.[9] In 2013, the UAE's population was 9.2 million, of which 1.4 million are Emirati citizens and 7.8 million are expatriates.[10][11][12]
Human occupation of the present UAE has been traced back to the emergence of anatomically modern humans from Africa some 125,000 BCE through finds at the Faya-1 site in Mleiha, Sharjah. Burial sites dating back to the Neolithic Age and the Bronze Age include the oldest known such inland site at Jebel Buhais. Known as Magan to the Sumerians, the area was home to a prosperous Bronze Age trading culture during the Umm Al Nar period, which traded between the Indus Valley, Bahrain and Mesopotamia as well as Iran, Bactria and the Levant. The ensuing Wadi Suq period and three Iron Ages saw the emergence of nomadism as well as the development of water management and irrigation systems supporting human settlement in both the coast and interior. The Islamic age of the UAE dates back to the expulsion of the Sasanians and the subsequent Battle of Dibba. The UAE's long history of trade led to the emergence of Julfar, in the present-day emirate of Ras Al Khaimah, as a major regional trading and maritime hub in the area. The maritime dominance of the Persian Gulf by Emirati traders led to conflicts with European powers, including the Portuguese and British.
Following decades of maritime conflict, the coastal emirates became known as the Trucial States with the signing of a Perpetual Treaty of Maritime Peace with the British in 1819 (ratified in 1853 and again in 1892), which established the Trucial States as a British Protectorate. This arrangement ended with independence and the establishment of the United Arab Emirates on 2 December 1971, immediately following the British withdrawal from its treaty obligations. Six emirates joined the UAE in 1971, the seventh, Ras Al Khaimah, joined the federation on 10 February 1972.[13]
Islam is the official religion and Arabic is the official language of the UAE. The UAE's oil reserves are the seventh-largest in the world while its natural gas reserves are the world's seventeenth-largest.[14][15] Sheikh Zayed, ruler of Abu Dhabi and the first President of the UAE, oversaw the development of the Emirates and steered oil revenues into healthcare, education and infrastructure.[16] The UAE's economy is the most diversified in the Gulf Cooperation Council, while its most populous city of Dubai is an important global city and international aviation and maritime trade hub.[17][18] Consequently, the country is much less reliant on oil and gas than in previous years and is economically focusing on tourism and business. The UAE government does not levy income tax although there is a system of corporate tax in place and value added tax was established in 2018 at 5%.[19]
The UAE's rising international profile has led to it being recognised as a regional and a middle power.[20][21] It is a member of the United Nations, the Arab League, the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, OPEC, the Non-Aligned Movement and the Gulf Cooperation Council.